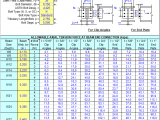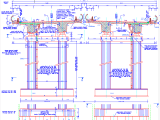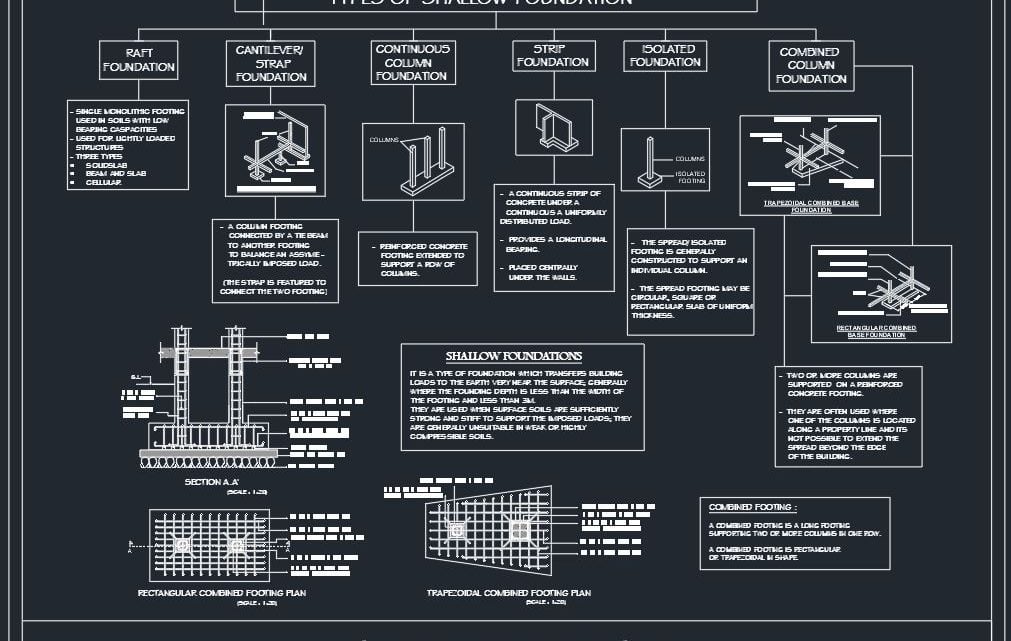
Types of Shallow Foundation Autocad Drawing
9 May 2025Table of Contents
Types of Shallow Foundation Autocad Drawing
Shallow foundation systems are one of the most widely used types of foundations in civil engineering. Whether you’re constructing residential buildings, small commercial structures, or light industrial facilities, understanding shallow foundations is essential for ensuring structural integrity and cost-efficiency. In this article, we’ll explore what a shallow foundation is, its types, when to use it, and the key benefits.
What Is a Shallow Foundation?
A shallow foundation is a type of building foundation that transfers structural loads to the earth very close to the surface, typically within 3 meters of the ground. Unlike deep foundations, which transfer loads to deeper soil layers or bedrock, shallow foundations rely on surface soil’s bearing capacity.
Key characteristics of shallow foundations:
-
Depth is less than the width of the foundation
-
Suitable for relatively light structures
-
Cost-effective and easier to construct
Types of Shallow Foundations
There are several types of shallow foundations, each designed for specific site conditions and building requirements:
1. Spread Footing (Isolated Footing)
-
Supports individual columns
-
Square or rectangular in shape
-
Common in residential and small commercial buildings
2. Combined Footing
-
Supports two or more columns when they are close to each other
-
Used when individual footings would overlap
3. Strip Footing
-
Continuous strip of concrete under a load-bearing wall
-
Ideal for masonry walls or structures with closely spaced columns
4. Mat or Raft Foundation
-
A large slab that supports multiple columns and walls
-
Spreads the load over a wide area
-
Used when soil bearing capacity is low or settlement needs to be minimized
5. Slab-on-Grade
-
Concrete slab poured directly at ground level
-
Often used in garages, warehouses, and low-rise buildings
When to Use a Shallow Foundation
Shallow foundations are suitable when:
-
The surface soil has good load-bearing capacity
-
Loads from the structure are relatively light
-
Site conditions do not require excavation to great depths
-
The water table is not too close to the surface
Ideal applications include:
-
Houses and bungalows
-
Low-rise apartments
-
Warehouses
-
Schools and small offices
Advantages of Shallow Foundations
Cost-Effective: Less excavation and material use compared to deep foundations.
Simple Construction: Easier and faster to build, even with basic equipment.
Accessibility: Ideal for locations with easy access and stable surface soil.
Time-Saving: Shorter project timelines due to quicker installation.
Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep if designed properly.
Key Considerations in Shallow Foundation Design
-
Soil Testing: Always conduct a geotechnical investigation to assess soil strength.
-
Load Calculations: Accurately determine structural loads to avoid settlement.
-
Drainage: Ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogging or soil erosion.
-
Frost Protection: In cold climates, build below the frost line to avoid heaving.
To download more Free Autocad Templates you can visit www.cadtemplates.org