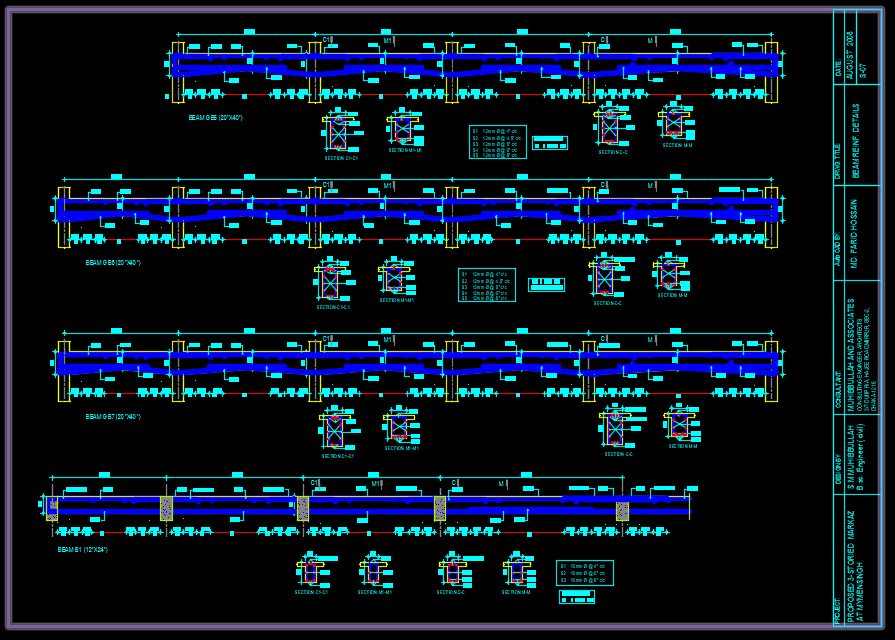
Large Precast Pile Sample Autocad Drawing
19 July 2025 Off By The Engineering CommunityTable of Contents
Large Precast Pile Sample Autocad Drawing
In the world of construction, a project is only as strong as its foundation. For structures built on challenging ground, a deep foundation system is essential to ensure stability and longevity. Among the various deep foundation solutions, precast concrete piles stand out as a reliable, efficient, and increasingly popular choice. This article delves into the world of precast piles, exploring what they are, their types, advantages, manufacturing process, installation, and wide-ranging applications.
What Are Precast Piles?
Precast concrete piles are structural members made from reinforced concrete that are manufactured off-site in a controlled factory environment.[1][2] Their primary purpose is to transfer the load of a structure through weak or unstable upper soil layers to a deeper, more competent soil or rock layer that can adequately support the weight.[3][4] These piles come in various shapes, with square, octagonal, and circular being the most common.[3][5]
Precast piles are a type of “displacement pile,” meaning that as they are driven into the ground, they displace the surrounding soil.[6] This process can have the added benefit of compacting granular soil, thereby increasing its bearing capacity.[5][6]
Types of Precast Piles
There are two primary categories of precast concrete piles, distinguished by their installation method:
-
Driven Precast Piles: This is the most common type. As the name suggests, these piles are driven or hammered into the ground using a pile driver.[1][4] They are forced into the earth until they reach a specified depth or level of resistance, ensuring a solid footing.
-
Bored Precast Piles: With this method, a hole is first drilled into the ground. The precast pile is then lowered into this borehole, and the space between the pile and the surrounding earth is filled with grout.[1][4] This technique is often preferred in situations where noise and vibration from pile driving must be minimized.[4]
The Advantages of Choosing Precast Piles
The decision to use precast piles comes with a host of benefits that can significantly impact a project’s timeline, budget, and quality.
Key Advantages:
-
Superior Quality Control: Because precast piles are manufactured in a factory setting, the production process is carefully controlled.[7][8] This ensures a consistent quality of concrete and accurate placement of reinforcement, which can be challenging to achieve with on-site-cast piles.[4][9]
-
Increased Speed and Efficiency: Piles are delivered to the construction site ready for installation.[10] This eliminates the time needed for on-site formwork, rebar placement, and concrete curing, leading to faster construction schedules.[6][7]
-
Exceptional Durability and Strength: Made from high-strength concrete and often prestressed, precast piles are highly durable and resistant to chemical and biological action from the soil.[5][9][11] They are well-suited for harsh environments, including marine and coastal applications.[10]
-
Cost-Effectiveness: For large-scale projects, the efficiency of mass production in a factory can make precast piles a very economical choice.[5][11]
-
Versatility in Application: Precast piles are suitable for a wide array of ground conditions and can be used for various types of structures.[6][12] They are particularly effective in very soft ground, contaminated soils, and for works over water like jetties and wharves.[6]
-
Minimal Site Disruption: Since the piles are manufactured off-site, there is no messy concrete work on the job site, and no spoil is generated from drilling, resulting in a cleaner and more organized work area.[6]
Potential Disadvantages to Consider
Despite their numerous advantages, there are some limitations to consider when planning to use precast piles.
Potential Drawbacks:
-
Transportation and Handling: Precast piles are heavy and bulky, requiring specialized equipment for transportation and maneuvering on-site.[4][9] Care must be taken during handling to prevent damage.[5][11]
-
Limited On-Site Adaptability: The length of the piles is determined at the factory.[9][11] If the required pile length on-site turns out to be different than anticipated, it can be difficult and costly to make adjustments.
-
Noise and Vibration: The process of driving piles into the ground can be very noisy and cause significant vibrations, which may not be suitable for densely populated or sensitive areas.[6]
-
Advance Planning is Crucial: Due to the off-site manufacturing and transportation requirements, significant lead time and planning are necessary.[6]
The Manufacturing Process: A Glimpse Behind the Scenes
The production of precast piles is a systematic process that ensures each pile meets stringent quality standards.
-
Mold Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of high-quality steel molds, or formworks, in the desired shape and size of the pile.[13]
-
Reinforcement Placement: A prefabricated steel reinforcement cage is carefully placed inside the mold.[8][13] For prestressed piles, high-tensile steel strands are tensioned within the mold before concrete is poured.[13]
-
Concrete Pouring: A precisely mixed, high-strength concrete is then poured into the molds.[8][13] The concrete is often vibrated to remove any air pockets and ensure a dense, solid pile.[13]
-
Curing: The concrete is then cured under controlled conditions, often using steam, to accelerate the hardening process and achieve the desired strength.[8][14]
-
Finishing and Inspection: Once cured, the piles are removed from the molds, inspected for any defects, and marked with identification details like length and casting date.[8][13]
Installation Methods for Precast Piles
Getting these substantial columns into the ground requires powerful equipment and precise techniques.
-
Driving: The most common method involves using an impact hammer or a vibratory driver to force the pile into the ground.[5][15] The pile is driven until it reaches a predetermined depth or a specific level of resistance, indicating it has reached a stable soil layer.
-
Jetting: In some cases, high-pressure water jets are used at the tip of the pile to help loosen the soil and aid in penetration.[5]
-
Pre-drilling/Pre-boring: For dense soil layers, a hole may be pre-drilled to a certain depth to make pile driving easier and reduce the required energy.[16]
Diverse Applications of Precast Piles
The strength and versatility of precast piles make them a go-to solution for a wide range of construction projects.
Common Uses Include:
-
Foundations for Buildings and Bridges: They provide essential support for high-rise buildings, bridges, and other large structures, especially in areas with poor soil conditions at the surface.[2][3][12]
-
Marine and Coastal Structures: Their high resistance to corrosion makes them ideal for building jetties, wharves, piers, and other structures in or near water.[6][10][16]
-
Infrastructure Projects: Precast piles are used to support wind turbines, power transmission towers, and railway and embankment structures.[2][6][16]
-
Retaining Walls: They can be used to provide lateral support for earth retention systems.[16]
In conclusion, precast concrete piles offer a powerful combination of quality, speed, and durability, making them a cornerstone of modern construction. By providing a solid and reliable deep foundation, they ensure the safety and stability of structures for generations to come, truly forming the bedrock of our built environment.
You can visit www.cadtemplates.org to download more free autocad templates