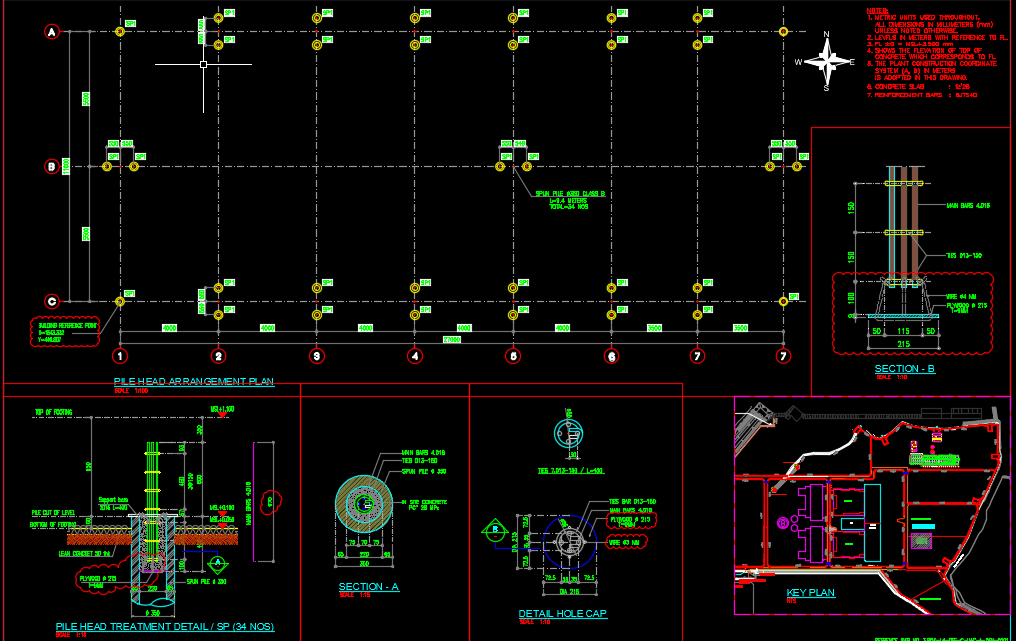
Pile Head Arrangement Plan Autocad Drawing
19 July 2025Pile Head Arrangement Plan Autocad Drawing
The stability and longevity of any major structure, from a towering skyscraper to a sprawling bridge, rests on the strength of its foundation. In the realm of deep foundations, the pile head arrangement is a critical component that ensures the structure’s load is safely and effectively transferred to the ground. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of pile head arrangement, its importance in structural engineering, and the key considerations for a robust and reliable design.
What is a Pile Head and Why is its Arrangement Crucial?
A pile is a long, slender column, typically made of concrete or steel, that is driven or drilled deep into the ground. Its purpose is to transfer the building’s load through weak upper soil layers to stronger, more stable soil or rock below.[1][2][3] The pile head is the upper end of the pile that connects it to the structure above.[4]
The arrangement of these pile heads and their connection to a pile cap—a thick concrete slab that links a group of piles together—is what constitutes the pile head arrangement.[5][6] This arrangement is not arbitrary; it is a meticulously planned design that is fundamental to the foundation’s performance for several reasons:
-
Even Load Distribution: Its primary function is to distribute the immense loads from the superstructure evenly across the group of piles.[1][4] This prevents any single pile from being overloaded, which could lead to failure.
-
Structural Stability: A well-designed arrangement provides lateral stability, resisting horizontal forces from wind, water, or seismic activity.[7]
-
Settlement Control: By distributing the load over a wider area, the pile head arrangement helps to minimize and equalize the settlement of the structure, preventing damaging differential settlement.[8]
-
Punching Shear Resistance: The pile cap, which is an integral part of the arrangement, helps to resist punching shear forces from the piles, a critical consideration in concrete floor slab design.[6][9]
Designing the Optimal Pile Head Arrangement
The design of a pile head arrangement is a complex process that involves collaboration between geotechnical and structural engineers. It requires careful consideration of numerous factors to ensure both safety and efficiency.
Key Design Considerations:
-
Number and Spacing of Piles: The number of piles required depends on the total load of the structure and the load-bearing capacity of each individual pile.[6] The spacing is also critical; a rule of thumb suggests a spacing of 2 to 3 times the pile diameter to prevent group failure, where the soil block around the piles fails.[2]
-
Pile Group Configuration: The geometric arrangement of the piles is determined by the number of piles and the goal of aligning the center of gravity of the pile group with that of the supported column or wall.[10] Common shapes include triangular for three piles, and rectangular or hexagonal for larger groups.[3][6]
-
Pile Type and Material: The choice between different pile types, such as driven displacement piles (timber, concrete, steel) or drilled piles (bored piles), will influence the design.[5][11] The material properties, like the strength of concrete or steel, are also fundamental inputs.[12]
-
Soil Conditions: A thorough geotechnical investigation is paramount. The type of soil, its load-bearing capacity, and the presence of weak or unstable layers will dictate the required depth and type of piles.[2]
-
Type of Loading: The nature of the loads—whether they are compressive, tensile (uplift), or involve bending moments—will significantly impact the design of the connection between the pile head and the pile cap.[13] For instance, tension piles require specific reinforcement to anchor them securely.[13][14]
-
Raker (Batter) Piles: To resist significant horizontal forces, some piles in the arrangement may be installed at an angle, known as raker or batter piles.[8][15]
Common Types of Pile Head Arrangements
The specific arrangement of pile heads is tailored to the project’s needs. Here are some fundamental types:
-
Single Pile Arrangement: Used when a single pile is sufficient to support the load. In this case, the pile head is directly connected to the foundation element above it.[4]
-
Group Pile Arrangement: This is the most common scenario, where multiple piles are connected by a single pile cap. This is essential for heavy structures like buildings and bridge piers to ensure even load distribution.[4][5]
-
Piled Raft Foundation: In this variation, the pile heads are integrated into a continuous foundation slab. This method can be cost-effective by reducing material and construction expenses while ensuring uniform load distribution.[3][4]
Construction and Execution: From Paper to Ground
The successful implementation of a pile head arrangement design requires precision and adherence to best practices during construction. The process generally involves:
-
Excavation: The area around the pile group is excavated to allow for the construction of the pile cap formwork.[3]
-
Pile Head Preparation: After the piles are driven or cast, their tops may need to be trimmed or broken to the correct level, ensuring a clean and sound concrete surface for the connection.[3][16] The reinforcing bars within concrete piles are often exposed to be tied into the pile cap reinforcement.[17]
-
Formwork and Reinforcement: Formwork is built around the pile heads, and a cage of steel reinforcement is placed and securely connected to the protruding reinforcement from the piles.[3]
-
Concreting: Concrete is then poured into the formwork to create the pile cap.
-
Curing: The concrete is allowed to cure and gain strength before the formwork is removed and construction of the superstructure proceeds.[18]
In conclusion, the pile head arrangement is far more than just a cluster of piles. It is a vital and meticulously engineered system that forms the bedrock of a structure’s stability. A deep understanding of the design principles, careful consideration of site-specific conditions, and precise execution are all essential to ensure that the foundation can reliably support the structure for its entire lifespan.
You can visit www.cadtemplates.org to download more free autocad templates