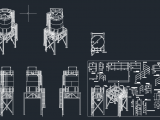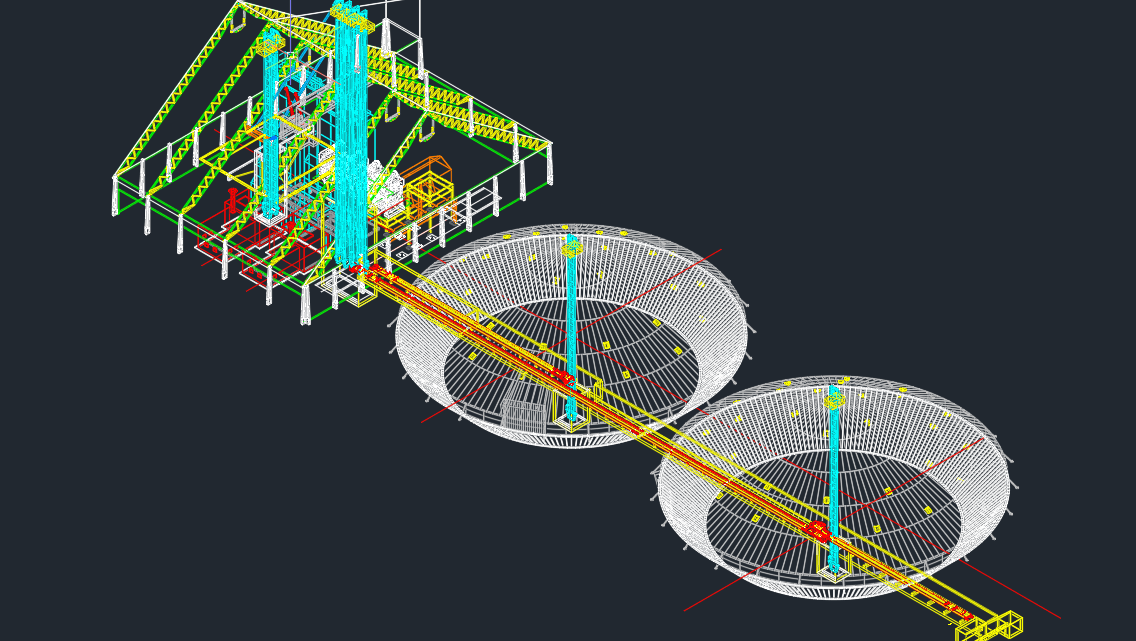
Silo Details 3D Plan – Autocad Drawing
5 August 2019Table of Contents
Silo Details 3D Plan – Autocad Drawing
Silo structures play a vital role in agriculture, industry, and construction by providing efficient storage solutions for bulk materials. Whether you’re storing grain, cement, coal, or wood pellets, silos are essential for preserving product quality, optimizing space, and ensuring safety. In this article, we’ll explore what silos are, the different types of silo structures, their design considerations, and common applications.
What Is a Silo Structure?
A silo is a tall, cylindrical or rectangular structure used for storing bulk materials. These structures are engineered to handle large volumes of dry materials in a controlled and safe manner. Silos are especially common in the agriculturaland industrial sectors, where they store commodities such as grain, flour, cement, fly ash, and other granular or powdered products.
Types of Silos
Silo structures are classified based on their design and purpose. The three main types include:
1. Tower Silos
These are vertical structures often seen on farms. Made from concrete, steel, or fiberglass, tower silos are great for storing silage, grain, and other agricultural products. They offer gravity-fed discharge and minimal footprint.
2. Bunker Silos
Bunker silos are horizontal and often constructed with concrete walls and a floor slab. They are ideal for high-volume storage and allow easy access for loading and unloading using heavy machinery.
3. Bag Silos
Flexible and portable, bag silos consist of long plastic tubes filled with silage. Though not permanent, they are cost-effective for seasonal or temporary storage needs.
Key Design Considerations
Designing a silo involves several critical factors:
-
Material type and flow characteristics
-
Storage volume requirements
-
Load calculations (vertical and lateral)
-
Moisture and temperature control
-
Ventilation and aeration systems
-
Foundation design and soil conditions
Engineers must also consider environmental factors, such as wind, seismic activity, and corrosion resistance, especially for outdoor silos.
Applications of Silo Structures
Silos serve various industries:
-
Agriculture: Storage of grains, feed, silage, and fertilizer.
-
Cement and Concrete Industry: Cement silos for batching plants and bulk material handling.
-
Mining and Quarrying: Storage of ores, coal, and aggregates.
-
Food Processing: Safe storage of flour, sugar, cocoa, and other powdered food products.
-
Energy Sector: Biomass and wood pellet storage for fuel.
Advantages of Using Silos
-
Efficient Space Utilization: Vertical storage saves floor space.
-
Product Protection: Shield materials from moisture, pests, and contamination.
-
Automation: Many silos integrate automated filling and discharge systems.
-
Cost-Effective: Reduce transportation and handling costs by enabling bulk storage on-site.
Conclusion
Silo structures are more than just storage units — they are engineered systems designed to improve operational efficiency, preserve product quality, and ensure safety. Whether you’re in farming, construction, or manufacturing, investing in the right type of silo can enhance your productivity and profitability.
To download more Free Autocad Files you can visit www.cadtemplates.org