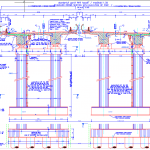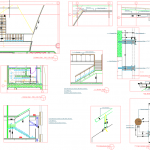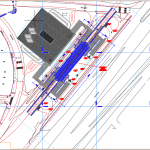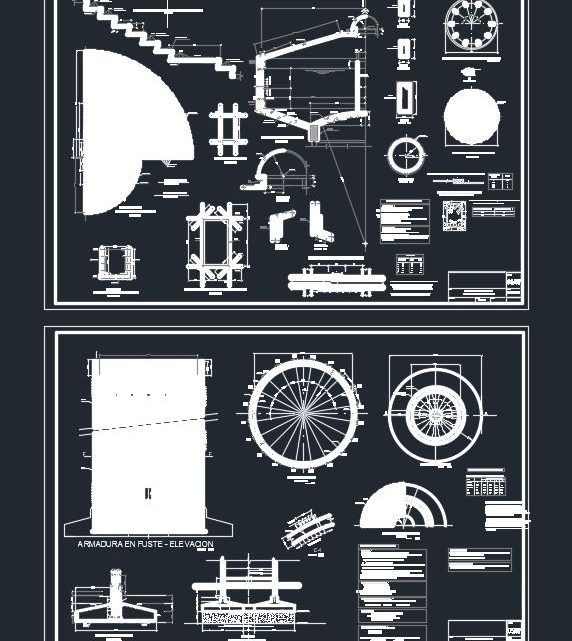
Elevated Tank Structural Details Autocad Drawing
5 May 2025Table of Contents
Elevated Tank Structural Details Autocad Drawing
In modern infrastructure, elevated water tanks play a crucial role in ensuring a reliable and steady water supply. Found in cities, rural areas, and industrial facilities alike, these elevated structures are far more than just giant containers on stilts — they’re vital components in water distribution systems. In this article, we’ll explore what elevated tanks are, why they’re important, how they’re designed, and the benefits they offer.
What Is an Elevated Tank?
An elevated tank is a water storage structure raised above ground level on a tower or support system. The height creates water pressure that allows water to flow through pipelines without the need for constant pumping. These tanks are often seen perched above schools, hospitals, industrial complexes, and municipal neighborhoods.
Why Elevated Tanks Are Essential
-
Constant Water Pressure:
The main advantage of elevated tanks is the ability to maintain consistent water pressure. Gravity does the work, reducing the need for energy-intensive pump systems. -
Emergency Storage:
During power outages or system failures, elevated tanks can still supply water for several hours or even days, depending on capacity. -
Fire Protection:
Elevated tanks are a critical part of fire safety systems, especially in remote or high-risk areas. They ensure enough water is available in emergencies. -
Operational Efficiency:
Because they reduce the need for continuous pumping, elevated tanks help municipalities and industries cut down on electricity costs.
Key Design Considerations
Designing an elevated tank requires attention to several engineering and environmental factors:
-
Capacity: Depends on daily water demand and emergency storage requirements.
-
Height: Determined by the pressure needed at the user’s tap; usually 20–30 meters is enough for residential systems.
-
Material: Common materials include steel, reinforced concrete, and sometimes composite materials.
-
Foundation: A strong foundation is essential to support the weight and resist environmental forces like wind and earthquakes.
-
Aesthetics: In urban areas, tanks may be designed with architectural features or painted to blend in with surroundings.
Types of Elevated Tanks
-
Spherical Tanks: Often used in high-pressure systems; aesthetically modern and compact.
-
Conical Bottom Tanks: Easy to clean and maintain, suitable for industrial applications.
-
Multi-column Tanks: Classic design with vertical columns; easier to construct and cost-effective.
-
Single-pedestal Tanks: Sleek, modern designs with a central column and storage dome on top.
Materials Used in Elevated Tanks
-
Steel: Durable and easy to fabricate but requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion.
-
Concrete: Excellent for large capacities; strong and long-lasting.
-
Composite Materials: Gaining popularity due to low maintenance and corrosion resistance.
Common Applications
-
Municipal Water Supply
-
Agricultural Irrigation Systems
-
Industrial Facilities
-
Emergency Firefighting Systems
-
Remote Communities and Camps
Maintenance and Inspection
To ensure long-term performance, elevated tanks require routine inspections. Engineers check for signs of corrosion, leaks, structural fatigue, and sediment build-up. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the tank but also ensures water quality remains high.
To download more Free Autocad Files you can visit www.cadtemplates.org