Types of Dams, advantages, disadvantages and classification
3 June 2019Table of Contents
Types of Dams, advantages, disadvantages and classification
What is a Dam?
A dam is a structure built across a stream, river or estuary to retain water. Dams are made from a variety of materials such as rock, steel and wood.
Structure of Dams:
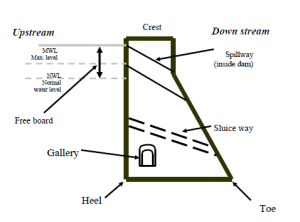
Fig 1 : Structure of Dams
Definitions:
- Heel: contact with the ground on the upstream side
- Toe: contact on the downstream side
- Abutment: Sides of the valley on which the structure of the dam rest.
- Galleries: small rooms like structure left within the dam for checking operations.
- Spillways: It is the arrangement near the top to release the excess water of the reservoir to downstream side
- Sluice way: An opening in the dam near the ground level, which is used to
clear the silt accumulation in the reservoir side.
Advantages of Dams:
- Dams gather drinking water for people -> Water Supply
- Dams help farmers bring water to their farms -> Irrigation
- Dams help create power and electricity from water -> Hydroelectric
- Dams keep areas from flooding -> Flood Control
- Dams create lakes for people to swim in and sail on -> Recreation & Navigation
Disadvantages of Dams:
- Dams detract from natural settings, ruin nature’s work
- Dams have inundated the spawning grounds of fish
- Dams have inhibited the seasonal migration of fish
- Dams have endangered some species of fish
- Dams may have inundated the potential for archaeological findings
- Reservoirs can foster diseases if not properly maintained
- Reservoir water can evaporate significantly
- Some researchers believe that reservoirs can cause earthquakes.
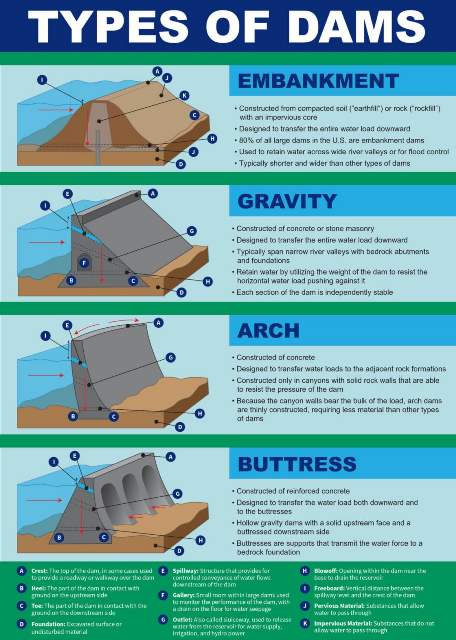
Classification of Dams:
Function
- Storage Dam
- Detention Dam
- Diversion Dam
- Coffer Dam
- Debris Dam
Hydraulic design
- Overflow Dam/Overfall Dam
- Non-Overflow Dam
Material of construction
- Rigid Dam
- Non Rigid Dam
Structural behavior
- Gravity Dam
- Arch Dam
- Buttress Dam
- Embankment Dam
- Rock-fill dam
1 – Gravity dams
Gravity dams are dams which resist the horizontal thrust of the water entirely by their own weight.
Concrete gravity dams are typically used to block streams through narrow gorges.
Material of Construction:
Concrete, Rubber Masonry
Fig 2 : Example of Gravity Dam Design
Fig 3 : The Grande Dixence Dam in 2004, facing west and Mont Blava (Source Wikipidea)
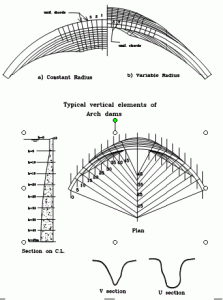
2- Arch Dam
An arch dam is a curved dam which is dependent upon arch action for its strength.
Arch dams are thinner and therefore require less material than any other type of dam.
Arch dams are good for sites that are narrow and have strong abutments.
Fig 4 : Jinping-I Dam also known as the Jinping-I Hydropower Station or Jinping 1st Cascade
Fig 5 : Typical vertical elements of Arch dams
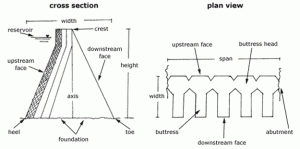
3- Buttress Dam
Buttress dams are dams in which the face is held up by a series of supports.
Buttress dams can take many forms – the face may be flat or curved.
Material of Construction: Concrete, Timber, Steel
Fig 6 : Design of buttress Dam
Fig 7 : Roselend Dam in France
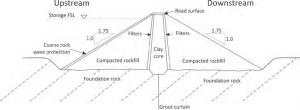
4- Embankment Dam
Embankment dams are massive dams made of earth or rock.
They rely on their weight to resist the flow of water.
Material of Construction: Earth, Rock
Fig 8: Embankment Dam Design
Fig 9 : Cross-sectional view of a typical earthen embankment dam
5- Rock-fill dam
These types of dams are made out of rocks and gravel and constructed so that water cannot leak from the upper stream side and through the middle of the structure. It is best suited in the area where rocks are around.
Fig 10 : Mohale Dam, Lesotho: highest concrete-face rock-fill dam in Africa
Read more about Dams: