Pervious Concrete – Advantages, Disadvantages and Application
20 November 2021Table of Contents
Pervious Concrete – Advantages, Disadvantages and Application
What is Pervious Concrete?
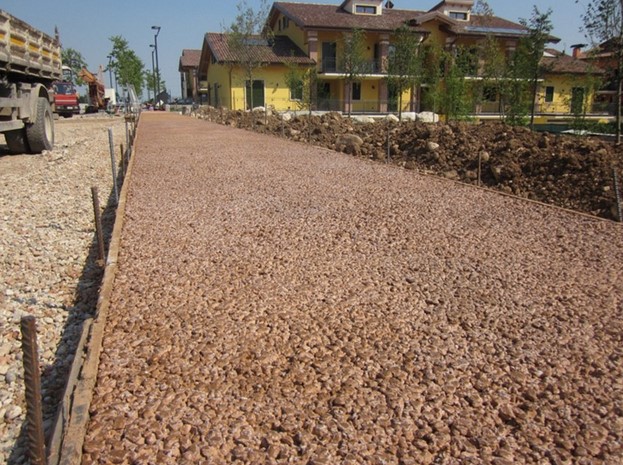
Pervious concrete has large voids that allow water or air to pass through it. The pores size varies from 2 to 8 mm, has a void content of 18 to 35 percent.
Further, pervious concrete has a compressive strength of 2.8-28.0 Moa (ACI 522,2010). Pervious concrete is also known as porous concrete or water-permeable concrete.
Like conventional concrete, its made from a mixture of cement, coarse aggregates, and water. However, it contains little or no sand, which results in a porous open-cell structure that water passes through readily.
Pervious concrete is often used in pavements. It is useful to recharge groundwater, minimizing stormwater run-off by enabling it to seep into the ground.
Consequently, it offers and advantage in resolving critical environmental challenges. Hence, a better effort towards sustainable development.
While the first use of pervious concrete dates back to the 1800s in Europe as pavement surface, it gained popularity in the US in the 1970s. Later, the demand for porous concrete increased after WWII as the cement supplies were badly affected. However, India realized the benefits of it in the 2000s.
Advantages Of Pervious Concrete
The primary advantage of pervious concrete is that it absorbs the stormwater. However, it serves multiple direct and indirect benefits as well.
1.Groundwater Recharge
The stormwater seeps through the pervious concrete and infiltrates through the ground. It ultimately adds up to the groundwater increasing groundwater level.
2.Reduction In Surface Run-off
The stormwater run-off reduces as the pervious concrete surface lets the water seep through it to the ground. Hence, the surface run-off reduces.
3.Reduction Of Sewers
Due to the reduced stormwater surface run-off, the size and need of the stormwater sewers reduce. Therefore, offering savings in drainage system costs.
4.Development of Trees
The stormwater infiltration through the ground provides higher moisture content. Moreover, the voids of the pervious concrete allow the necessary air for roots to breathe. Consequently, offering a healthier environment for roots to grow into trees and plants.
5.Filtering Of Stormwater
The pervious concrete acts as a filter for the stormwater. The dirt gets trapped into voids, and hence only clear water reaches the stream, pond or lake.
Disadvantages Of Pervious Concrete
- Can not be used in pavements with heavy traffic flow.
- Requires longer curing time.
- Difficult to find out water content in fresh concrete.
- Conventional concrete tests like slump test, compaction factor test are not applicable.
- Requires specialized construction practice.
- Special design considerations need to be implemented.
- Requires regular cleaning to maintain its permeability
APPLICATIONS OF POROUS CONCRETE:
- Residential roads, streets, and driveways.
- Low-volume pavements.
- Sideways and avenues.
- Parking area.
- Tennis Court.
- Sub-base for traditional concrete pavements.
- In Well linings.
- Swimming pool decks.