Cladding for Tall Buildings
8 February 2020Cladding for Tall Buildings
Cladding is prefabricated panels that are attached to the structural frame of the building. The main function of cladding is to prevent the transmission of sound, provide thermal insulation, create an external facade, and prevent the spread of fire.
There are different cladding systems, such as curtain wall, metal curtain, stone cladding, brick claddings, precast concrete, and timber cladding.
Cladding systems are non structural elements. However, cladding can play a structural role in transferring wind loads, impact loads, and self-weight back to the structural framework. In particular, wind causes positive and negative pressure on the surface of buildings, so cladding must be designed to have adequate strength and stiffness to resist this load, both in terms of the type of cladding selected and its connections back to the structure.
Particularly in tall buildings, the wind pressure on the glazing is one of the important design considerations, this is because if one glazing fails, when it is fallings off, it will also hit the glazing on the below floors, which will cause a continues failure of the glazing.
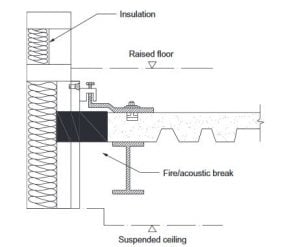
Fig.1 shows the typical connection between the facade to structural members. On tall buildings, access systems must be provided to cladding system allowing regular inspection, maintenance, cleaning, and replacement (in particular, replacement of external seals).
Fig.1.Connection details of cladding to structural members
Curtain wall are used widely for tall buildings. Typically, curtain wall systems comprise a light weight frame onto which glazed or opaque infill panels can be fixed. These infill panels are often described as ‘glazing’ whether or not they are made of glass as shown in Figs.2 and 3.
Fig.2.A typical cladding of a tall building in Hague, Netherland
Fig.3. A glass curtain wall example of a building in Delft, Netherland
The frames play an important role in transferring loads back to the primary structure of the building and accommodating differential movement and deflection. Therefore, needs to be designed in detail. In some companies, therefore special fac ade design team to handle it.