Large-displacement piles Advantages and Disadvantages
2 January 2021Large-displacement piles Advantages and Disadvantages
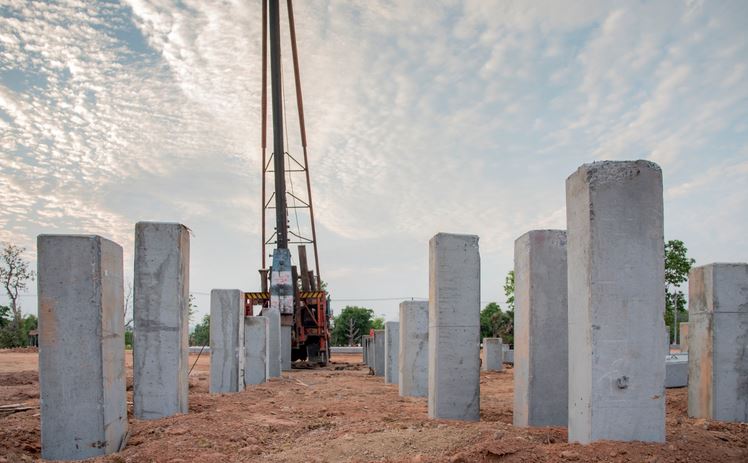
Large-displacement piles include all solid piles, including precast concrete piles, and steel or concrete tubes closed at the lower end by a driving shoe or a plug, i.e. cast-in-place piles.
Advantages of Displacement Piles
- Material of preformed section can be inspected before driving.
- Steel piles and driven cast-in-place concrete piles are adaptable to variable driving
- Installation is generally unaffected by groundwater condition.
- Soil disposal is not necessary.
- Driving records may be correlated withinsitu tests or borehole data.
- Displacement piles tend to compact granular soils thereby improving bearing capacity and stiffness.
- Pile projection above ground level and the water level is useful for marine structures and obviates the need to cast insitu columns above the piles.
- Driven cast-in-place piles are associated with low material cost.
Disadvantages of Displacement Piles
- Pile section may be damaged during driving.
- Founding soil cannot be inspected to confirm the ground conditions as interpreted from the ground investigation data.
- Ground displacement may cause movement of, or damage to, adjacent piles, structures, slopes or utility installations.
- Noise may prove unacceptable in a built-up environment.
- Vibration may prove unacceptable due to presence of sensitive structures, utility installations or machinery nearby.
- Piles cannot be easily driven in sites with restricted headroom.
- Excess pore water pressure may develop during driving resulting in false set of the piles, or negative skin friction on piles upon dissipation of excess pore water pressure.
- Length of precast concrete piles may be constrained by transportation or size of casting yard.
- Heavy piling plant may require extensive site preparation to construct a suitable piling platform in sites with poor ground conditions.
- Underground obstructions cannot be coped with easily.
- For driven cast-in-place piles, the fresh concrete is exposed to various types of potential damage, such as necking, ground intrusions due to displaced soil and possible damage due to driving of adjacent piles.